The other day I was in the bookstore browsing the books in
the Politics section when I came across a book titled “Drink”. I was reminded of a book called “blink” which
argued that the best decisions people make are snap decisions. That book was answered with another book
called “think” that argued people should take time to think before making a
decision. So, I thought, the message of
this book is clearly: Forget all that thinking, just “Drink”.
I laughed out loud at myself in public like I’m prone to do
and picked up the book. I glanced at the
cover and at the very top it said “The Intimate Relationship Between Women and
Alcohol”.
Uh oh.
Nevertheless my interest was piqued.
In the first paragraph a rarely mentioned truth is revealed:
“Over the past few decades, the feminist revolution has had enormous
ramifications. Women outnumber their
male counterparts in postsecondary education in most of the developed world,
and they are about to do the same in the workplace.” Interesting. Could this be a feminist book
that actually tells the truth? (Despite this truth, however, women-only
scholarships are abundant as are such programs designed to get more women into
the sciences—which, by the way, are already dominated by women with the
exception of the math-heavy domains.
Men-only scholarships are virtually if not actually non-existent).
“But what has not been fully documented or explored is that
while women have gained equality in many arenas, they also have begun to close
the gender gap in terms of alcohol abuse.”
Please take note of where women stand on this. Far more women than men? No.
Same number of women as men?
No. Actually it’s still more men
than women, but now the difference between those numbers is smaller (at least
according to this author).
Just how close is that gender gap? 1.2 men for every 1 woman,
1.1 men for every woman? Well, according
to CDC statistics, in the US it’s 3:1 men to women. Wait… what? Yeah, three times as many men die
in alcohol related deaths as women.
From the CDC: “In 2010, a total of 25,692 persons died of
alcohol-induced causes in the United States.
This category includes deaths from dependent and nondependent use of
alcohol, as well as deaths from accidental poisoning by alcohol. It excludes unintentional injuries,
homicides, and other causes indirectly related to alcohol use, as well as
deaths due to fetal alcohol syndrome. … For males, the age-adjusted death rate
for alcohol-induced causes in 2010 was three times the rate for females.” CDC source
If you are like me, you are probably thinking, well, that’s
just the US, how does that compare to the rest of the world? According to The WHO: “The harmful use of alcohol
is a particularly grave threat to men.
It is the leading risk factor for death in males ages 15 – 59, mainly
due to injuries, violence, and cardiovascular diseases. Globally, 6.2% of all male deaths are
attributable to alcohol, compared to 1.1% of female deaths. Men also have far greater rates of total
burden attributed to alcohol than women—7.4% for men compared to 1.4% for
women. Men outnumber women four to one
in weekly episodes of heavy drinking—most probably the reason for their higher
death and disability rates. Men also have
much lower rates of abstinence compared to women. Lower socioeconomic status and educational
levels result in a greater risk of alcohol-related death, disease, and injury—a
social determinant that is greater for men than women.” WHO source
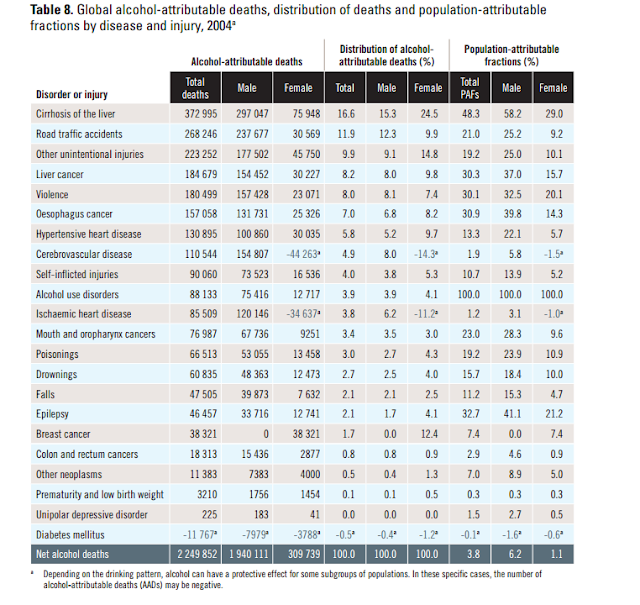
Table 8 from the WHO shows that 1,940,111 global deaths were
male while 309,739 were female (in 2004).
That means, worldwide 6.3 male deaths per every 1 female death is
attributable to alcohol.
What does the author have to say about this? Well, naturally she is concerned about men’s
health and how not only are men falling behind in postsecondary education they
will soon be falling behind in employment, but nevertheless men still suffer in
greater numbers from alcoholism.
A rational mind would draw such a conclusion.
A feminist mind, well, just read between the lines: LINE
feminists are not rational LINE.
According to the WHO, in every category (except Breast
Cancer) the number of male deaths is greater than the number of female
deaths. In fact, in most cases, the
number of male deaths is several times greater than that of female deaths.
What does this imply to the author? The effects of alcohol on women constitute a “crisis”
that will have a “far-reaching impact on society”. It’s “an epidemic we can no longer afford to
ignore”.
My sympathies to anyone who is or knows someone affected by
alcohol. I’m sorry that the author or
anyone has to go through this (my family has also experienced its share of
alcoholism). However, that’s no excuse
for what appears to me to be outright lies.
Granted, I haven’t read the book, just the dust jacket, but if that is
indication of the contents that lie within, then there’s certainly no evidence
for “in-depth research” and there is certainly nothing “ground-breaking” about
feminists taking an issue that affects women at a fractional rate compared to
men and calling it a crisis.
Last, but not least, I want to call attention to the fact
that the author was virtually ecstatic about how feminism has led to larger
numbers of women than men in postsecondary education. According to the WHO “lower socioeconomic
status and education levels result in a greater risk of alcohol-related death”. So, not only have women outstripped men in
educational attainment, there is a very real link that lower educational
attainment increases the risk of alcohol-related death for men. Yet, somehow, beyond all of this, beyond the
fractional mortality numbers, beyond the fact that men are being virtually shouldered
out of college by women (a factor that can lead to alcoholism), this is still,
somehow, a “crisis” for women.
Dust Jacket Full Text
Over the past few decades, the feminist revolution has had
enormous ramifications. Women outnumber
their male counterparts in postsecondary education in most of the developed
world, and they are about to do the same in the workplace. But what has not been fully documented or
explored is that while women have gained equality in many arenas, they also
have begun to close the gender gap in terms of alcohol abuse. In the United States alone, more than
twenty-three thousand women die from heavy drinking each year. Binge drinking and so-called drunkorexia are
on the rise, contributing exponentially to an array of health conditions and
cancers.
Combining in-depth research with her own personal story of
recovery, Ann Dowsett Johnston delivers a ground-breaking examination of a
shocking yet little-recognized epidemic threatening society today, what
preeminent researcher Sharon Wilsnack believes is a “global epidemic” of women’s
drinking.
Dowsett Johnston’s authority comes from a place of
experience. Eight years ago she was an
award-winning senior journalist with Canada’s major newsweekly magazine Maclean’s
and popular on the speaking circuit. She
seemed to have it all when she was named vice principal of McGill
University. In private, the high-functioning
professional knew she was wrestling with a demon that had undone her own
mother: alcohol addiction. Dowsett
Johnston took a very private exit from her professional life and went to
rehab. She reentered professional life
in 2010, winning the prestigious Atkinson Fellowship in Public Policy, charged
with examining the closing gender gap in the world of risky drinking. Sober now for five years, she retells her
struggles with brutal honesty, affording us an unprecedented look at women and
drinking that is both moving and enlightening.
Dowsett Johnston dissects the psychological, social, and
workplace factors that have contributed to this crisis, exploring their
far-reaching impact on society at large and individual lives, including her
own. Comprehensive and emotionally
riveting, Drink is sure to become a modern classic on the topic of women and
drinking, much as Andrew Solomon’s The Noonday Demon was for depression. Drink is a brave and powerful story
beautifully told and an important investigation into an epidemic that we can no
longer afford to ignore.